C programming recursion; In this tutorial, you will learn recursive functions in c programming with the help of definition, syntax, advantages, disadvantages, uses, and examples.
C Recursion
- Recursion Function
- Syntax of Recursive Function
- Flowchart of Recursion
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
- Example 1 – C Program to Find Factorial of a Number Using Recursive Function
- Example 2 – C program print first n Fibonacci numbers using recursion
Recursive Function
In C programming, a function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
Syntax of Recursive Function
Syntax of recursive function in c programming; as follows:
returntype recursive_func ([argument list])
{
statements;
... ... ...
recursive_func ([actual argument]);
... ... ...
}
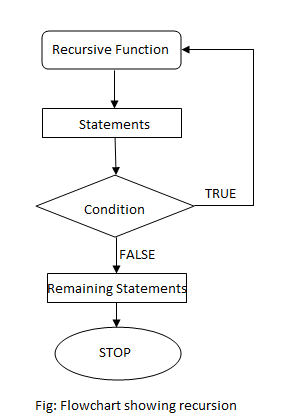
Flowchart of Recursion
Flowchart of recursion function; as follows:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
Advantages of recursion
- 1. The code may be easier to write.
- 2. To solve such problems which are naturally recursive such as tower of Hanoi.
- 3. Reduce unnecessary calling of function.
- 4. Extremely useful when applying the same solution.
- 5. Recursion reduce the length of code.
- 6. It is very useful in solving the data structure problem.
- 7. Stacks evolutions and infix, prefix, postfix evaluations etc.
Disadvantages of recursion
- 1. Recursive functions are generally slower than non-recursive function.
- 2. It may require a lot of memory space to hold intermediate results on the system stacks.
- 3. Hard to analyze or understand the code.
- 4. It is not more efficient in terms of space and time complexity.
- 5. The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not properly checked.
Example 1 – C Program to Find Factorial of a Number Using Recursive Function
#include<stdio.h>
long int multiplyNumbers(int n);
int main() {
int n;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Factorial of %d = %ld", n, multiplyNumbers(n));
return 0;
}
long int multiplyNumbers(int n) {
if (n>=1)
return n*multiplyNumbers(n-1);
else
return 1;
}
Output
Enter a positive integer: 6 Factorial of 6 = 720
Example 2 – C program print first n Fibonacci numbers using recursion
#include<stdio.h>
int fibo(int num)
{
if(num==1||num==2)
return 1;
else
return (fibo(num-1)+fibo(num-2)); // recursive call
}
int main()
{
int i,n;
printf("Enter the required term: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("First %d fibonacci numbers aren",n);
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
printf("%dn",fibo(i));
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the required term: 7 First 7 fibonacci numbers are 1 1 2 3 5 8 13
